
You did your homework, picked a great stock, totally undervalued and ready for a nice price rise. However, after you bought the stock, the damn thing goes and drops 20%.
So what do you do now? Do you sell it and cut your losses or do you hold on and hope that it recovers? Do you double down?
Those are the only scenarios available to stock investor. Luckily as option traders, we have a much larger arsenal at our disposal. Today we are looking at the stock repair strategy.
Contents
- Introduction
- How A Stock Repair Strategy Works
- Option Assignment And Settlement
- Determining Strike Prices
- Real World Example
- Summary
Introduction
Assuming the goal of the investor is to simply recover the losses and get out at breakeven, a strategy called the Stock Repair Strategy can be employed.
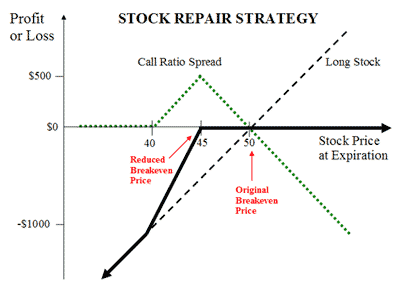
The strategy involves adding a call ratio spread to the stock holding. Here’s what it looks like.

Image Credit: The Options Guide
In this example, the investor purchased shares at $50 only to see it drop 20% to $40.
Holding on to the stock would require a gain of 25% to get back to the breakeven of $50. Or the investor could purchase more shares at $40, but that involves allocating a lot more capital to a losing position. Not a good idea.
How A Stock Repair Strategy Works
The idea with the stock repair strategy is that the investor can reduce the breakeven price without adding any more capital to the trade. There is no additional downside risk with the trade.
By implementing a 2:1 call ratio spread, the investor can lower the breakeven to $45. Hopefully they can do this at no cost or a small debit.
For example if the $40 calls are trading at $2 and the $45 calls at $1, the stock repair strategy will cost nothing to implement. Here’s some more examples:
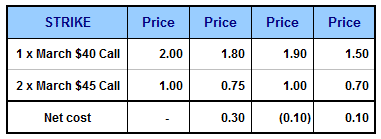
You can see that the strategy is generally going to cost very little to implement.
For simplicity, let’s assume the $40 call cost $2 and the $45 calls cost $1. Let’s look at five possible scenarios at the expiry of the options.
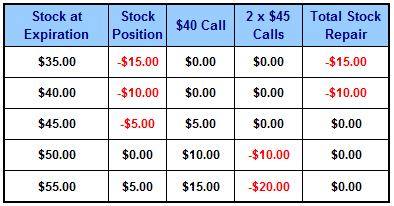
Stock Falls to $35
If the stock closes at $35 at option expiration, the $40 call and $45 calls both expire worthless.
As the net cost of the options was $0, the investor is in the same position as if they had just held the stock. Note however, they are much better off than the investor who doubled down.
Stock Remains at $40
If the stock closes at $40, all of the call options will again expire worthless. The stock repair strategy has had no impact and the investor is in the same position.
Stock Rises to $45
This is a really good situation for the investor who used the stock repair strategy. The $45 calls will be exactly at-the-money and will expire worthless.
The $40 call will have an intrinsic value of $5. Assuming the investor can sell the call for $5 they have made a total profit of $5 on the options (remember the trade cost nothing).
The long stock position has risen $5 but is still below the breakeven price of $50. The investor still shows a loss of $5 on his stock holding.
So, taking the $5 loss on the stock and the $5 gain from the options, the investor is perfectly at breakeven. In other words, the breakeven has been reduced to $45 compared to $50.
The investor who just held the stock would still be stuck with a loss of $5.
Stock Rises to $50
In this scenario, the stock is back to breakeven, but what about our stock repair strategy.
The $45 calls will be worth -$10 and the $40 call will be worth $10, so the net value of the options equals $0. So in this scenario, just holding the stock and using the repair strategy would perform the same.
Stock Rises to $55
In this scenario, the stock repair strategy would underperform simply holding the stock. Keep in mind, the stock would need to rise 37.5% in this situation for this scenario to occur. So traders would need to weigh up how likely that is.
At this level, the $45 calls would be worth -$20 and the $40 call would be worth $15 for a loss of $5 on the options.
The stock is now showing a $5 gain, so the overall position is flat.
Here is a graphical summary of the five scenarios:
Option Assignment And Settlement
It’s important to remember that if the stock does rise about $45 before expiry, traders could be exposed to early assignment risk. Traders may want to close the options prior to expiry in this case.
At expiry, if the stock if above the strike price of the sold calls and the investor wants to hold on to their shares, they will need to close both of the sold calls and the bought call.
Or they may choose to exit their shares by allowing them to be called away through one of the sold calls. They would then need to close the remaining sold call and bought call.
Determining Strike Prices
The CBOE has some excellent information on determining strike prices for the stock repair strategy. They suggest the distance between the strikes should be half of the loss suffered on the stock.
In our example, the stock was showing a loss of $10 and the strikes were $5 apart.
If the loss was $20, the strikes should be $10 apart etc.
Generally the bought call is placed at-the-money or as close to as possible.
Real World Example
Let’s look at an example using a stock that has been under pressure in recent months – Paypal (PYPL).
Assuming a trader was unlucky enough to buy into PYPL stock at 230, they would be sitting on a considerable loss with the stock closing at 184.89 yesterday.
As a stock trader, they would need the stock to recover to 230, to get back to break-even.
However, by using options, we can lower the break-even price to 210, without adding any extra risk to the trade.
Here’s how it can be done:
Buy 1 February 190 call @ 12.55
Sell 2 February 210 calls @ 6.30
Buying the 190 call costs $1,255 and selling two of the 210 calls receives a credit of $1,260. The net result for placing the trade is a $5 credit.
Because the trade is placed for a credit, there is no additional risk to the downside. If PYPL stays below 190, the call options expire worthless, and the trader still owns the 100 shares of stock.
The break-even price has also been reduced to 210.
If the stock ends up between 190 and 230, the combined stock repair strategy will outperform the pure stock position.
The tradeoff is that any potential gains above 230 are lost.
Here you can see the risk graph before the adjustment:
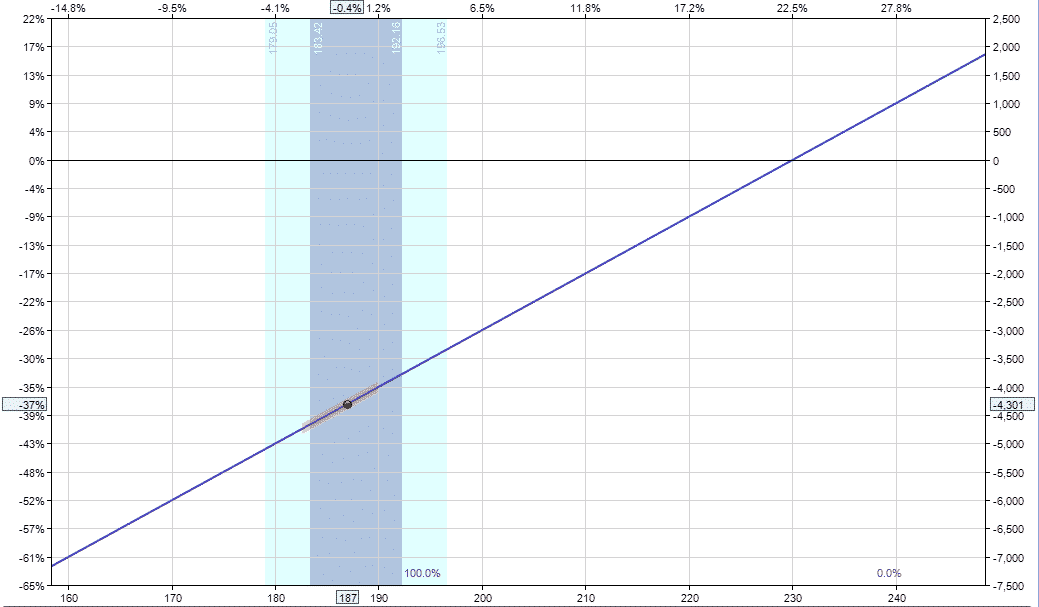
This shows the proposed adjustment, so we can see the difference between the live trade and the adjusted trade.
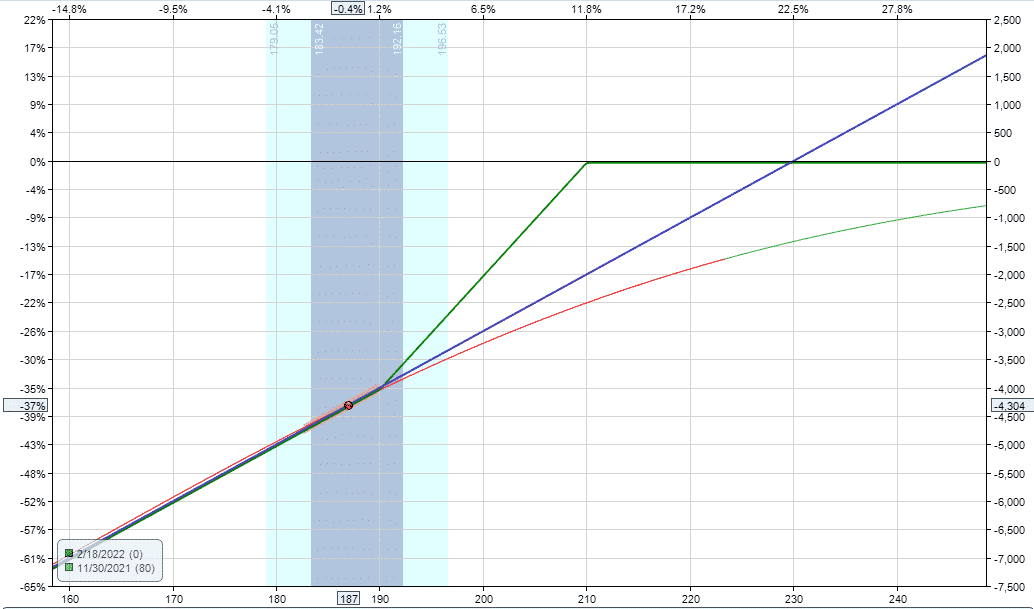
And this shows the trade after adding the stock repair strategy:
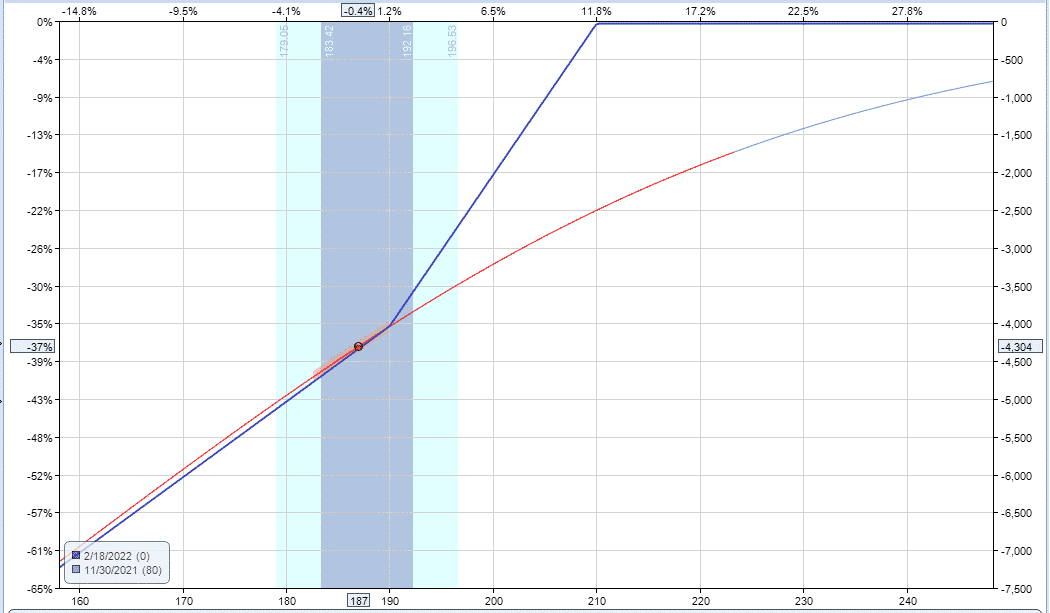
Summary
Today we’ve learned that the stock repair strategy is ideal for an investor who is holding a losing stock who simply wants to get back to breakeven and get out.
It can help the investor reduce their breakeven price for little or no cost.
The strategy does not protect the investor from further downside, but it may be a more attractive proposition than “doubling down”.
When placing the stock repair strategy, the investor is giving up any potential upside on the stock.
Watch the video below to see me go through a couple of live examples:
Trade safe!
Disclaimer: The information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice. The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.











Hi, Gavin,
a 2:1 call ratio spread in this case means that:
-buy one 40calls
-sell two 45 calls.
If it is right, what is the proper/preferable expiration date?i
It depends on your outlook. As with most trades, the shorter dated ratio spreads will have bigger P&L fluctuations than longer dated spreads.
Gavin, Do you have courses, videos, or info on “How to Trade “OPTIONS ON FUTURES”? Please let me know.
Thanks
Hi Herman, I’m going to be releasing a free series here on the blog over the next few weeks on futures and options on futures, so keep an eye out.
Hi Gav,
will y be able to explian to me the following on the call ratio spread on PYPL
“The break-even price has also been reduced to 210.” How did the expiration of the short call reduced the breakeven to 210??
The extra long call helps reduce the breakeven price.